Piet Mondrian (1872 – 1944)
Get a Mondrian Certificate of Authenticity for your painting (COA) for your Mondrian drawing.
For all your Mondrian artworks you need a Certificate of Authenticity (COA) in order to sell, to insure or to donate for a tax deduction.
Getting a Mondrian Certificate of Authenticity (COA) is easy. Just send us photos and dimensions and tell us what you know about the origin or history of your Mondrian painting or drawing.
If you want to sell your Mondrian painting or drawing use our selling services. We offer Mondrian selling help, selling advice, private treaty sales and full brokerage.
We have been authenticating Mondrian and issuing certificates of authenticity since 2002. We are recognized Mondrian experts and Mondrian certified appraisers. We issue COAs and appraisals for all Mondrian artworks.
Our Mondrian paintings and drawings authentications are accepted and respected worldwide.
Each COA is backed by in-depth research and analysis authentication reports.
The Mondrian certificates of authenticity we issue are based on solid, reliable and fully referenced art investigations, authentication research, analytical work and forensic studies.
We are available to examine your Mondrian painting or drawing anywhere in the world.
You will generally receive your certificates of authenticity and authentication report within two weeks. Some complicated cases with difficult to research Mondrian paintings or drawings take longer.
Our clients include Mondrian collectors, investors, tax authorities, insurance adjusters, appraisers, valuers, auctioneers, Federal agencies and many law firms.
We perform Piet Mondrian art authentication, appraisal, certificates of authenticity (COA), analysis, research, scientific tests, full art authentications. We will help you sell your Piet Mondrian or we will sell it for you.
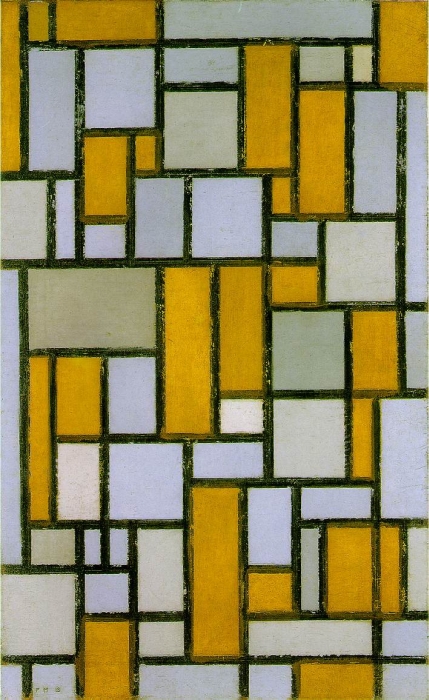

1918 Oil on canvas 80.2 x 49.9 cm Museum of Fine Arts, Houston, Texas
Piet Mondrian was a Dutch artist of the De Stijl movement. While Theo van Doesberg founded the De Stijl movement, Mondrian defined a new branch of art known as Neo-Plasticism.

1921 Oil on canvas 39 x 35 cm
Mondrian was born in Amersfoort, Netherlands but soon moved with his family to Winterswijk. In 1892 Mondrian moved to Amsterdam to study at the Academy of Fine Art. While studying, Mondrian worked as a primary school teacher to support himself. As a student, Mondrian painted in a representational manner, creating realistic or impressionistic landscape studies. Many of Mondrian’s early paintings are in the collection of The Hague’s Gemeenemuseum.
1935-42 Oil on canvas 101 x 51 cm
1939-42 Oil on canvas 80 x 73 cm Private collection
In 1908 Mondrian began to study the theosophical movement, guided by Helena Petrovna Blavatsky. Mondrian’s interest in spirituality remained an important factor throughout his life and career.

1942-43 Oil on canvas 127 x 127 cm The Museum of Modern Art, New York
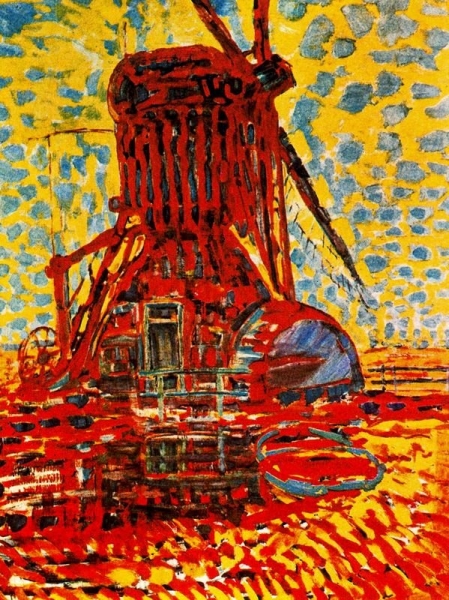

1911 Oil on Canvas 114 x 87 cm Gemeentemuseum, La Haya
Another inspirational force in Mondrian’s work was the 1911 Moderne Kunstkring exhibition of Cubism. After seeing this exhibit Mondrian began to simplify his work and use geometrical forms. Around this same time Mondrian decided to leave Amsterdam and move to Paris, where he studied Cubism and changed the spelling of his name from ‘Mondriaan’ to ‘Mondrian’.

1913 Oil on Canvas 79.5 x 63.5 cm Museum Thyssen Bornemisza
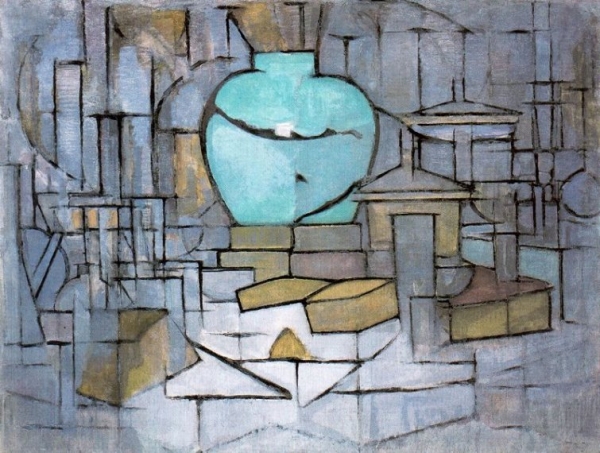

1912 Oil on Canvas 95.2 x 120 cm Guggenheim Museum, New York
In 1914 at the start of World War I, Mondrian returned to the Netherlands. Back in his home country, Mondrian found his place at the Laren artist’s colony, working alongside Bart van der Leck and Theo van Doesberg. In the next couple of years Mondrian was able to release a twelve-piece publication known as “The New Plastic” expressing his views on artistic theory.
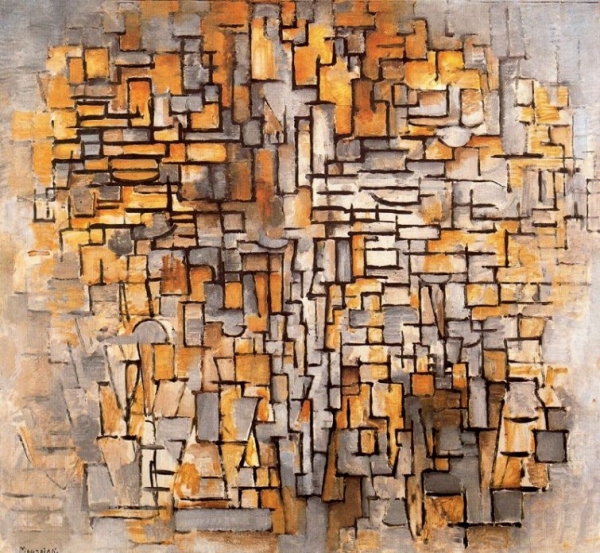

1913 Oil on Canvas 104.4 x 113.6 Guggenheim Museum, New York
After the war in 1919 Mondrian was free to leave the Netherlands and returned to France, where he remained for nearly twenty years. At this point Mondrian began painting his iconic grid-based paintings, painting. His early grid paintings contain grays and more subtle tones, where his later pieces use a black grid and primary colors.

1925 Oil on Canvas 75 x 65 cm Private Collection, Zurich
Throughout the 1920s Mondrian continued to refine his style of abstraction. Examples of experimentation can be seen in his “lozenge” works, in which he tilted square canvasses at a forty-five degree angle.
1942 Oil on Canvas 120 x 144 cm Harry Holtzman Collection, New York
In 1938 Mondrian left Paris to escape the spread of fascism and relocated to London for a brief amount of time before moving to New York City. While Mondrian only spent a few years in New York City he made a great impression on the art scene. The Museum of Modern Art in New York has held several exhibitions of his work and owns many pieces in its private collection. Mondrian’s work is now is Modern art collections around the world. Do you think you own a painting by Mondrian? Contact us. We are the experts on Piet Mondrian.
Reviews
1,217 global ratings
5 Star
4 Star
3 Star
2 Star
1 Star
Your evaluation is very important to us. Thank you.
